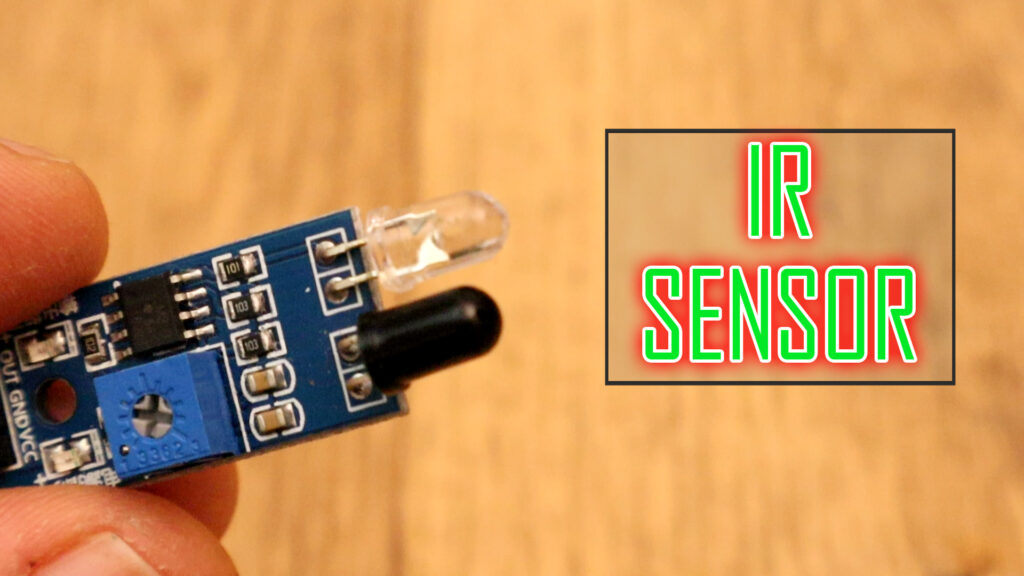
Hello Guys! In this blog, Today we will discuss about IR Sensor Module. How this module works, Pin Diagram/Pinout, Hardware Overview, IR Sensor Module Circuit Diagram, Working Principle, Specifications, and Applications.
Introduction
The IR Sensor Module or infrared (IR) sensor is a basic and most popular sensor in electronics. It is used in wireless technology like remote controlling functions and detection of surrounding objects/ obstacles. IR sensors mainly consist of an Infrared(IR) LED and a Photodiode, this pair is generally called IR pair. An IR LED is a special-purpose LED, it is can emit infrared rays ranging from 700 nm to 1 mm wavelength. These types of rays are invisible to our eyes. In contrast, a photodiode or IR Receiver LED detects the infrared rays.
IR Sensor Module Pin Diagram/Pinout

| Pin No | Pin Name | Description |
|
1 |
VCC |
+5 v power supply |
|
2 |
GND |
Ground (-) power supply |
|
3 |
OUT |
Digital Output |
IR Sensor Module Hardware Overview

The IR sensor module consists mainly of the 1. IR Transmitter, 2. Photodiode Receiver, 3. LM393 Comparators IC, 4. Variable Resistor (Trim pot), 5. Power LED, 6. Output LED.
1. Infrared LED or IR Transmitter:
An IR LED is a specially designed light-emitting diode (LED), it’s emitting infrared rays. Infrared ray’s wavelength ranges from 700 nm to 1 mm. Normally an IR LED looks like a normal LED. It has two terminals, the longer one is Positive and the smaller one is negative. When IR LED operates at a power supply, it starts emitting infrared rays.

2. Photodiode Receiver Or IR Receiver
Normally IR receivers are photodiodes. It is a semiconductor that has a P-N junction. A photodiode is capable of detecting infrared rays. It’s operated in Reverse Bias. The photodiode has very High resistance in the absence of infrared rays and becomes low when infrared rays fall on it. Also, It has two terminals, the longer one is Positive and the smaller one is negative.

4. Variable Resistor (Trim pot)
IR sensor has an onboard variable resistor(potentiometer). This variable resistor is a 10k preset. It is used to set the range of operation. Rotate the preset knob to adjust the detection distance, the effective operation range is 2-10 cm. If the preset knob is rotated clockwise, the detection range will be increased. If it rotates counterclockwise, the detection range will be decreased.

5. Power LED
This onboard LED indicates the IR Sensor power supply is ON or OFF. When we turn on the IR Sensor power supply this RED LED is also turn on.
6. Output LED:
When infrared is reflected back to the IR receiver and the sensor detects an obstacle, the green LED lights up. So, the Green LED is used to indicate the sensor senses an obstacle.
How to make an IR Sensor Module
Components Required
| Components Name | Quantity |
| IC: LM358 or LM393 (You can choose any one of these ICs) | 1 |
| IR (Infrared) LED (IR-TX) | 1 |
| Photodiode (IR-RX) | 1 |
| 1K Resistor (R1, R4) | 2 |
| 100-ohm Resistor (R2) | 1 |
| 10K Resistor (R3) | 1 |
| 10K Potentiometer (VR1) | 1 |
| 0.1 uF Ceramic Capacitor (C1, C2) | 2 |
| Red LED (D1) | 1 |
| Green LED (D2) | 1 |
IR Sensor Module Circuit Diagram
How IR Sensor Module Works
When we connect the IR sensor module to 5v power supply. At the same time, Infrared LED (IR-TX) starts emitting infrared rays. Then set the threshold voltage at the Non-Inverting input (3) of the IC by rotating the potentiometer knob for setting the sensor sensitivity.
If infrared rays reach to object’s surface and some of the radiation reflected back to the IR receiver (IR-RX). The Photodiode or IR receiver (IR-RX) detects the infrared light.

When reflected infrared light Falls on the Photodiode, the resistance of the photodiode falls down from a huge value and the voltage across the photodiode drops. So, a High amount of voltage from the photodiode is given to the Inverting input (2) of the IC. Then the LM393/LM358 IC compares this voltage with the threshold voltage. In this condition, the Inverting input voltage is greater than the Non-Inverting input voltage so the IC output is Low (0). So, the sensor output is Low (0).
When the Photodiode or IR receiver (IR-RX) does not detect the infrared light, then the resistance of the photodiode will be very high. So, a Low amount of voltage from the photodiode is given to the Inverting input (2) of the IC. Then the LM393/LM358 IC compares this voltage with the threshold voltage. In this condition, the Inverting input voltage is less than the Non-Inverting input voltage so the IC output is High (1). So, the sensor output is High (1).
Sensor Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|
Operating voltage |
5V or 3.3V DC |
|
Comparator chip |
LM393 |
|
Output type |
Digital and Analog output |
|
Obstacle detection range |
2cm to 20cm |
|
Detection angle |
35 degree |
|
PCB size |
3.1cm x 1.5cm |
Diverse Applications of IR Sensors
In various applications, infrared (IR) sensors find extensive use. These applications include:
- Temperature Measurement: Use IR sensors to measure an object’s or surface’s temperature by detecting the infrared radiation they emit. This method is precious in ovens, HVAC systems, and industrial process control applications.
- Motion Detection: Use IR sensors to detect the movement of objects, including people. They are useful in security systems, automated lighting, and industrial automation.
- Proximity Sensing: Utilize IR sensors for detecting objects close to the sensor, which is especially useful in applications like automatic doors and mobile devices.
- Distance Measurement: Utilize IR sensors to measure the distance to an object by emitting a beam of infrared radiation and measuring the reflected radiation received by the sensor.
- Other Applications: IR sensors serve diverse purposes, extending to remote controls, automotive collision avoidance systems, and robotics.
It’s worth noting that IR sensors represent just one type capable of detecting and measuring infrared radiation. Other sensor types, such as thermal cameras, can also serve this purpose.