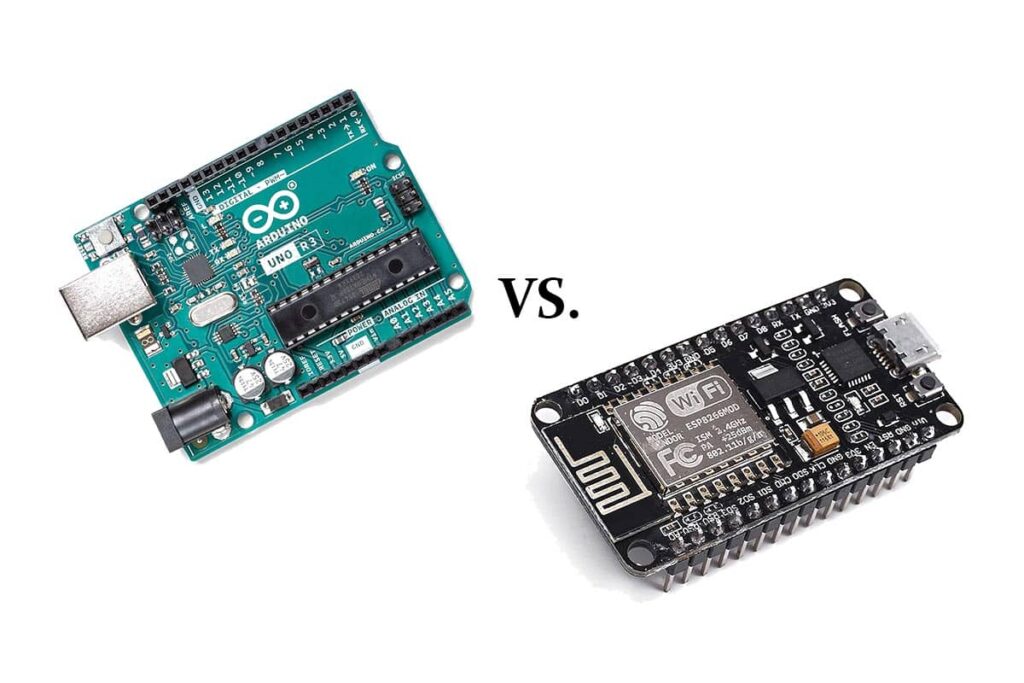
Choosing between NodeMCU ESP8266 and Arduino for your project involves considering various factors, including features, capabilities, ease of use, and compatibility. Both platforms are popular choices for embedded systems and IoT projects, but they have distinct characteristics. This guide aims to help you make an informed decision based on your specific project requirements.
NodeMCU ESP8266:
a. Overview:
NodeMCU is an open-source IoT platform based on the ESP8266 WiFi module. It combines the capabilities of the ESP8266 microcontroller with the simplicity of the Lua scripting language.
b. Key Features:
-
- WiFi Connectivity: NodeMCU comes with built-in WiFi capabilities, making it suitable for IoT projects that require wireless communication.
-
- Lua Scripting: Programmed using Lua scripts, which can be advantageous for those familiar with Lua or prefer a scripting language.
c. Pros:
-
- Integrated WiFi: Ideal for projects requiring wireless connectivity.
-
- Cost-Effective: NodeMCU boards are generally affordable.
-
- Rapid Prototyping: Quick development and prototyping with Lua scripting.
d. Cons:
-
- Limited Analog Pins: NodeMCU has fewer analog pins compared to some Arduino boards.
-
- Lua Learning Curve: Learning Lua might be necessary for those unfamiliar with the language.
Arduino:
a. Overview:
Arduino is an open-source electronics platform based on easy-to-use hardware and software. It is widely used for developing interactive electronic projects.
b. Key Features:
-
- Diverse Boards: Arduino offers a variety of boards with different features and capabilities.
-
- Large Community: Extensive community support, vast libraries, and a wealth of documentation.
-
- C/C++ Programming: Programmed using the Arduino IDE, which uses a simplified version of C/C++.
c. Pros:
-
- Versatility: Arduino supports a wide range of applications and projects.
-
- Abundant Libraries: Extensive libraries simplify code development.
-
- Community Support: A large and active community for assistance.
d. Cons:
-
- No Built-in WiFi: Some Arduino boards lack built-in WiFi, requiring additional modules for wireless connectivity.
-
- Cost: Some feature-rich Arduino boards can be more expensive than basic NodeMCU boards.
Arduino VS NodeMCU: Detailed Comparision
| NodeMCU | Arduino UNO | |
| Microcontroller | Node MCU ESP8266 | ATmega328p |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V | 5V |
| Input Voltage | 4.5V-10V | 7V-12V |
| Current consumption | 15uA – 400mA | 45mA – 80 |
| Current consumption in Deep Sleep | 0.5uA | 35mA |
| Digital I/O Pins | 16 | 14 |
| Digital I/O Pins with PWM | 16 | 6 |
| Analog Input Pins | 1 | 6 |
| SPI | 2 | 1 |
| I2C | 1 | 1 |
| UART | 2 | 1 |
| DC Current per I/O Pin | 12mA | 40mA |
| Flash Memory | 4 MB | 32 kb |
| SRAM | 64 kb | 2 kb |
| EEPROM | 512 Bytes | 1024 Bytes |
| Clock speed | 80 MHz | 16 Mhz |
| Length | 58 mm | 69 mm |
| Width | 31 mm | 53 mm |
| Wifi | Yes | No |
| Power Jack | No | Yes |
| USB connection | Micro-USB | USB type-B |
NodeMCU vs Arduino Uno – Specs
RAM
NodeMCU: 128KB
Ardiuno Uno: 2KB
ROM (Flash Memory)
NodeMCU: 4MB
Arduino Uno: 32KB
Processor
NodeMCU: 32-bit
Arduino Uno: 8-bit
Processor Speed
NodeMCU: 80MHz
Ardiuno Uno: 16MHz
Wireless Communication
NodeMCU: ESP8266 SoC
Arduino Uno: None
Serial Communication
NodeMCU: UART / I2C / SPI
Arduino Uno: UART / I2C / SPI
GPIO
NodeMCU: 9 Digital (3.3V), 1 Analog (1.8V)
Arduino Uno: 10 Digital (5V), 6 Analog (2.5V)
Dimensions / Form Factor
NodeMCU: 4.8 x 2.5 cm
Arduino Uno: 6.8 cm × 5.3 cm
Choosing the Right Platform:
NodeMCU
When to choose the NodeMCU:
-
- If you have a budget constraint
-
- If you need specific features like WiFi
-
- If you need to run a complex sketch or algorithm
-
- If you need a compact prototype – on a breadboard or similar
Arduino Uno
When to choose the Arduino Uno:
-
- If you are an absolute beginner
-
- If you want to try interfacing with various sensors and modules
-
- If you are learning the basics
-
- If you need more GPIOs
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the choice between NodeMCU ESP8266 and Arduino depends on the specific requirements of your project. If built-in WiFi is crucial, and you favor Lua scripting for rapid development, NodeMCU is a strong contender. On the other hand, Arduino offers versatility, a robust community, and various board options, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Consider your project’s needs, your familiarity with programming languages, and the desired features to make the most informed decision.



I like this web site very much, Its a rattling nice office to read and get
information.