Microcontrollers are everywhere, whether you’re driving your car, on your computer reading this (or smartphone/tablet), or making a cup of coffee on your coffee machine. With IoT rapidly increasing and data constantly being gathered, microcontrollers are a huge part of the modern world.
What is a Microcontroller?
A microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of NOR flash, OTP ROM or ferroelectric RAM is also often included on chip, as well as a small amount of RAM. Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications, in contrast to the microprocessors used in personal computers or other general-purpose applications consisting of various discrete chips.
In modern terminology, a microcontroller is similar to, but less sophisticated than, a system on a chip (SoC). A SoC may include a microcontroller as one of its components, but usually integrates it with advanced peripherals like a graphics processing unit (GPU), a Wi-Fi module, or one or more coprocessors.
Inside a Microcontroller: Essential Components
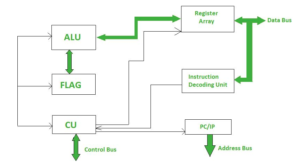
A microcontroller can be seen as a small computer, and this is because of the essential components inside of it; the Central Processing Unit (CPU), the Random-Access Memory (RAM), the Flash Memory, the Serial Bus Interface, the Input/Output Ports (I/O Ports), and in many cases, the Electrical Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM). Figure 1 shows a great diagram of the main parts and also other parts in the microcontroller. Let’s dive into each of these components and see how they work inside the microcontroller.
Types of Microcontroller:
Here are some of the most common types of microcontrollers:
- 8-bit Microcontrollers: These are the most basic type of microcontrollers, typically used in simple applications such as toys, small appliances, and remote controls. They have a limited processing power and memory capacity, but they are easy to use and cost-effective.
- 16-bit Microcontrollers: These are more advanced than 8-bit microcontrollers and are capable of performing more complex tasks. They are commonly used in applications such as medical devices, automotive systems, and industrial control systems.
- 32-bit Microcontrollers: These are the most powerful and feature-rich microcontrollers, capable of handling large amounts of data and performing high-speed processing. They are used in applications such as gaming systems, multimedia devices, and high-end industrial automation.
- ARM Microcontrollers: These microcontrollers are based on the ARM architecture and are widely used in a variety of applications, including mobile devices, automotive systems, and industrial control systems.
- PIC Microcontrollers: These microcontrollers are manufactured by Microchip Technology and are commonly used in a wide range of applications, including home appliances, automotive systems, and medical devices.
- AVR Microcontrollers: These microcontrollers are manufactured by Atmel Corporation and are commonly used in applications such as robotics, industrial control systems, and consumer electronics.
- FPGA-based Microcontrollers: These microcontrollers use field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) to provide highly customizable and flexible processing capabilities. They are commonly used in applications such as digital signal processing, video processing, and high-speed networking.
- CPU: The microcontroller is referred to as a CPU device since it is utilized to carry and decode data before effectively completing the assigned duty. All microcontroller components are connected to a specific system utilizing a central processing unit. The CPU can decode instructions retrieved from the programmable memory.
- Memory: The memory chip of a microcontroller functions similarly to a microprocessor in that it stores all of the data as well as programming. Microcontrollers have a limited quantity of RAM/ROM/flash memory for storing program source code.
- Input and Output ports: In general, these ports are used to interface or otherwise drive various appliances like LEDs, LCDs, printers, and so on.
- Serial Ports: Serial ports are used to offer serial interfaces between the microcontroller and a range of additional peripherals, such as the parallel port.
- Timers: Timers and counters are included in a microcontroller. In a microcontroller, they are used to manage all timing and counting activities. The fundamental function of a counter is to count external pulses, whereas timers conduct clock tasks, pulse production, modulations, frequency measurement, and oscillations, among other things.
- ADC (Analog to Digital Converter): ADC is an acronym for Automated Data Collection (Analog to Digital Converter). Analog to digital converter is abbreviated as ADC. The primary function of an ADC is to convert analog signals to digital signals. The required input signals for ADC are analog, and the resulting digital signal is employed in a variety of digital applications such as measurement equipment.
- Control Interpretation: This controller is used to provide delayed control to a running application, with internal or external interpretation.
- Block with Special Functions: A specific function block is included in some special microcontrollers built for particular devices such as robots and space systems. This block has additional ports for doing specific tasks.
Uses of Microcontroller:
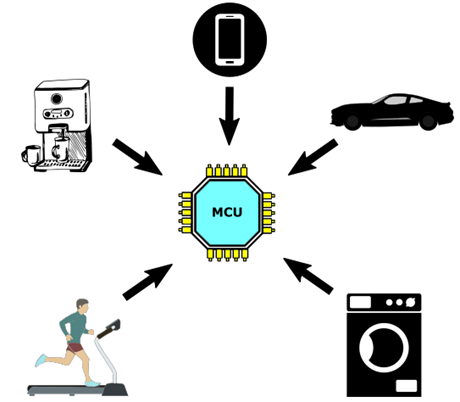
Microcontrollers are used in a wide range of electronic devices and systems, including:
- Home Appliances: Many home appliances, such as washing machines, refrigerators, and air conditioners, use microcontrollers to perform various functions, such as temperature control, timing, and monitoring.
- Automotive Systems: Microcontrollers are used in automotive systems, such as engine control units, anti-lock braking systems, and airbag systems, to control various functions and ensure safe and efficient operation.
- Medical Devices: Medical devices, such as insulin pumps, heart monitors, and blood glucose meters, use microcontrollers to perform various functions and provide accurate and reliable results.
- Industrial Control Systems: Microcontrollers are used in industrial control systems, such as robotics, process control systems, and manufacturing equipment, to control and monitor various processes and operations.
- Consumer Electronics: Many consumer electronics devices, such as digital cameras, gaming systems, and audio players, use microcontrollers to perform various functions and provide advanced features and capabilities.
- IoT Devices: Internet of Things (IoT) devices, such as smart home systems, wearables, and environmental sensors, use microcontrollers to connect to the internet and perform various functions.
- Aerospace and Defense Systems: Microcontrollers are used in aerospace and defense systems, such as satellites, avionics, and missiles, to control and monitor various functions and ensure safe and efficient operation.
Microcontroller Properties :
- Microcontroller devices are capable of having words longer than 64 bits.
- Microcontroller consist of RAM , ROM , Timer , I/O Ports.
- Microcontroller ROM is used for program storage and RAM is used for data storage.
- It is designed by using CISC architecture.
- The power consumption of modern microcontrollers is significantly lower and have operating voltage range from 1.8V to 5.5V
- The latest feature of microcontroller is flash memory like EPROM and EEPROM.
- The most recent feature of a microcontroller is flash memory, such as EPROM and EEPROM.