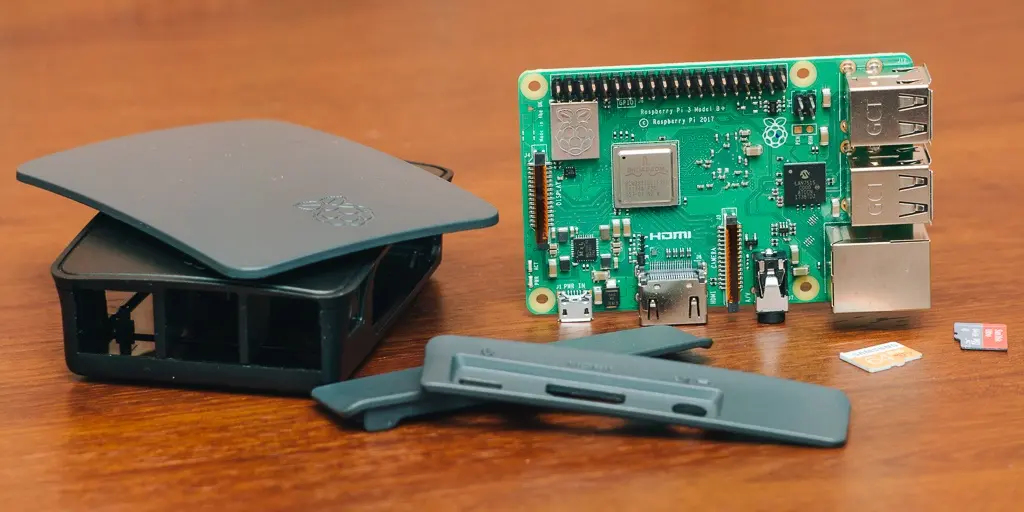
Microcomputers are electronic devices that hold a microprocessor inside of them that act as their CPU, or central processing unit. CPUs execute all arithmetic and logic unit functions and allow computers to follow instructions from users. Microcomputers are relatively small because of their smaller CPU and include a memory unit, a microprocessor, and an input and output unit on a singular printed circuit board.
Micro-computers are small and relatively inexpensive computers with a central processing unit (CPU) made up of a microprocessor. The computer also includes Micro and input and output (I/O) circuity. It is a complete computer utilized on a small scale and designed for a single person.
Microcomputers are the outmoded name for personal computers (PC) or devices based on a single-chip microprocessor. Common microcomputers include laptops and desktops. Apart from these standard PCs, microcomputers include calculators, mobile phones, notebooks, workstations, and embedded systems.
These tiny machines are smaller than a mainframe or minicomputer. A microcomputer utilizes a single combined semiconductor chip for its Central Processing Unit (CPU). Read-only memory (ROM) and Random Access Memory (RAM) are the two types of memory these types of computers use. Input/output (I/O) ports, and a bus or system of interconnecting wires, are all housed in a single unit, generally known as a motherboard.
What are the benefits of using microcomputers?
There are a variety of benefits of using microcomputers, including:
Connection
All microcomputers allow internet connectivity. As a result, anyone using a microcomputer can explore the internet, send messages to others, watch movies, and stream music, among other functions. This allows for an easy, cordless, and convenient way to use the internet.
Cost
Microcomputers can vary in cost, but some may be more affordable for consumers. As many people use different types of microcomputers every day and the supply and demand increase, the cost to make, distribute, and sell them may be less expensive. It’s important to note that this can vary based on a specific production company or distributor.
Portability
In most cases, microcomputers are easily portable. Devices such as laptop computers, smartphones, and tablets are lightweight and convenient to carry. The nature of their size, build, and weight can allow you to use the internet wherever you’d like.
Types of Microcomputers
There are several types of microcomputers that people use for both professional and personal purposes. These microcomputers range in size, weight, capabilities, and purpose, but all hold a microprocessor that allows them to function effectively and successfully. The most common types of microcomputers typically include:
Laptop computer
Laptop computers are easily transportable personal computers that people can use for whatever they’d like. Usually, they’re slim and can have a built-in screen, keyboard and mouse, which helps people use them during travel. Laptops vary in size and weight, and people can use them for school, work, or personal purposes.
Desktop computer
Desktop computers are another type of personal computer despite technically being larger than a standard laptop. This type of microcomputer is common in the workplace and in other professional settings. Desktop computers are cube-shaped and have an accompanying monitor to view outputs.
Smartphones
Smartphones are small, easily portable electronic devices that allow you to make phone calls, send text messages, and use the internet. Many people use smartphones for both personal and professional purposes, and there are a variety of different from which to choose. Smartphones offer a convenient means of using the internet and communicating with others.
Computer workstation
Computer workstations are common in workplaces and professional settings. Typically, this type of microcomputer is more high-end and shares data on a network, such as a server. In most cases, computer workstations directly connect to other computers in the network, and the network administrator can control them remotely.
Personal digital assistant (PDA)
A personal digital assistant, usually referred to simply as a PDA or a handheld PC, is a microcomputer that acts chiefly as a digital information manager. This type of microcomputer is like a smartphone in that you can use it to make phone calls and connect to the internet, but it offers a stylus and drawing option so you can use it to write information. Personal digital assistants have various mobile information storage features and offer several professional uses, including for health care positions.
Tablets
A tablet is a handheld, portable electronic device, similar to a smartphone but typically without phone call capability. This type of microcomputer is common for both professional and personal purposes and sometimes acts as a substitute for laptops. People use tablets to read books and magazines, take photos, create visual designs, communicate with others and do other related activities on a larger surface than smartphones offer.
Server microcomputer
Microcomputers can also function as servers. A server microcomputer is a microcomputer that actually distributes data to computers that are connected to the network. Typically, this type of microcomputer holds large quantities of data to send to connected computers on request.
Applications of Microcomputer
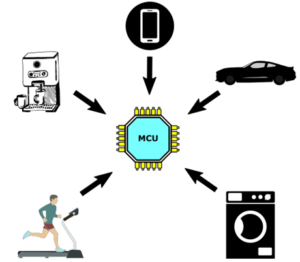
Home and personal use: Microcomputers are commonly used in households for personal use, such as browsing the internet, creating and editing documents, watching videos, and playing games.
Education: Educational institutions widely use microcomputers for teaching, research, and administration. They are used to create and deliver educational content, facilitate online learning, and manage student records.
Business and office use: Microcomputers are used in offices for various tasks, such as creating and editing documents, spreadsheets, presentations, and databases, as well as for communication and networking.
Scientific and engineering applications: Microcomputers such as simulations, data analysis, and control systems are used in scientific and engineering applications.
Entertainment: Microcomputers are used in the entertainment industry for tasks such as music and video production, gaming, and virtual reality.
Healthcare: Microcomputers are used in healthcare for tasks such as managing patient records, medical imaging, and telemedicine.
Industrial control systems: Microcomputers are used in industrial control systems for process control, automation, and monitoring tasks.
Embedded systems: Microcomputers are used in various embedded systems, such as consumer electronics, automotive systems, and home automation systems.