With all the powerful and fun to use development boards out there, there’s a lot you can do without a breadboard. However, if you’re setting up small circuits for learning the basics of electronics or need a place for peripheral components, breadboard is a great tool to have.
What is a Breadboard?
A Breadboard is simply a board for prototyping or building circuits on. It allows you to place components and connections on the board to make circuits without soldering. The holes in the breadboard take care of your connections by physically holding onto parts or wires where you put them and electrically connecting them inside the board. The ease of use and speed are great for learning and quick prototyping of simple circuits. More complex circuits and high-frequency circuits are less suited to breadboarding. Breadboard circuits are also not ideal for long-term use like circuits built on perfboard (protoboard) or PCB (printed circuit board), but they also don’t have the soldering (protoboard), or design and manufacturing costs (PCBs).
Why is it called a Breadboard?
In the before times, boards used in the kitchen for cutting bread were used by young circuit designers to build circuits on with screws or nails driven into the board with wires wrapped around them to complete circuits. This was an improvement on ‘deadbug’ or direct solder connections, since the circuit could be nailed down and secure as well as easily modified if necessary for debugging or enhancements. The name has stuck through to today, even though placing circuits on boards for bread is only done for Instagram posts.
Why do you use a BreadBoard?
A breadboard is handy because you can set up circuits quickly and temporarily to test them and move on to a more permanent arrangement after investigating how it works on the breadboard. They are great for hobbyists and tinkerers to set up projects as a standalone device, or as a peripheral to an Arduino, Raspberry Pi, LaunchPad, BeagleBone, and many other development boards. They come in many sizes to fit projects large and small. Breadboards are also inexpensive, and the parts that work with them are also typically inexpensive too. If you want to make your project more permanent, moving from a design on a breadboard to protoboard or PCB will be easier than skipping to those harder to manipulate boards.
If you’re just getting started, or are well down the path of electronic design, you’ll run across breadboards. Getting to know their strengths of quick and easy circuit creation, and their weaknesses of impermanence and limitations in terms of power handling and RLC (resistance, inductance, capacitance) effects will help you create many fun and useful projects later.
Types of Breadboard
There are two types of the breadboard, namely Solderless and solder breadboard.
Let’s discuss the above two types of the breadboard in detail.
Solderless breadboards
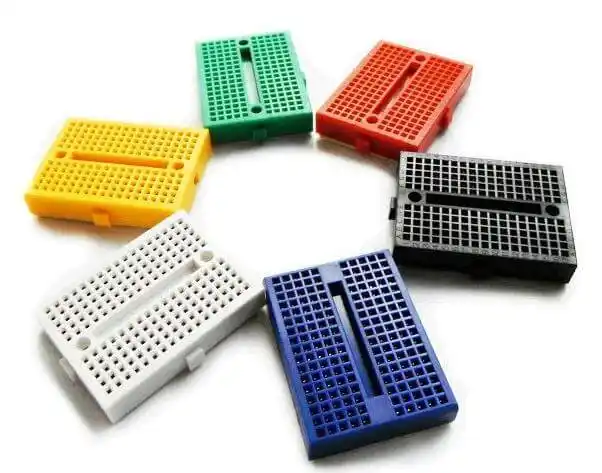 AAs the name implies, Solderless boards do not require any soldering after the electronic components are plugged in. The leads or ends of the components are inserted into the holes of a breadboard for its functioning.
AAs the name implies, Solderless boards do not require any soldering after the electronic components are plugged in. The leads or ends of the components are inserted into the holes of a breadboard for its functioning.
Solder breadboard
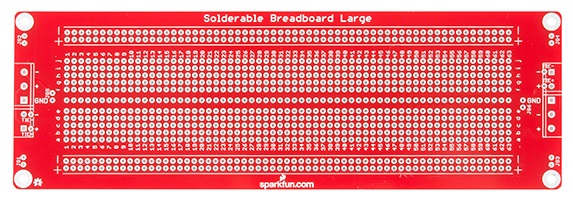
The solder breadboard is also a board that has a tiny hole embedded into it. We can insert the terminal of the electronic components into the board. After the connection is rechecked, we can solder these components.
The common difference between solder and Solderless breadboards is the reusability.
Advantages of Breadboard
The advantages of using breadboard are listed below:
-
Temporary prototypeWe can build a temporary prototype for the projects with the help of a breadboard.
-
ReusableToday, Solderless boards are mostly used in various applications. It does not require any soldering to fix the components. Hence, it can be reused.
-
LightweightThe breadboard is made of white plastic, which is light in weight.
-
Easy experimentationWe can quickly insert the leads of the components into the tiny holes of the breadboard. The circuit can be created using various components and circuit design.
-
InexpensiveThe breadboards are easily available. It also cost less.
-
Easy to useIt does not involve any complex parts. We can easily insert the required number of components.
-
No drilling requiredThe hoes are already embedded in the board. Hence, we do not require any drilling to insert the electronic components.
-
Quick modifying capabilityWe can easily switch or remove the components from the board.
-
Available in various sizesThe breadboards are available in various sizes. We can select the desired size as per the number of components.
-
Easy to adjust.The breadboard is easy to adjust in the project or connection setup.
Disadvantages of Breadboard
The disadvantages or limitations of the breadboard are listed below:
-
Not suited for high current applications
-
Low-frequency Solderless boards are limited to low-frequency applications.
-
Requires more physical space for simple circuits.
-
A high number of connections in the Solderless board make the circuit messy due to a greater number of wires.
-
The circuit design does not work well for high-speed design.
-
The plugging and unplugging can disturb the other connections.
-
Less reliable connections.
-
Limited signaling.



I like this website it’s a master piece!